Sunday, December 16, 2007
Comment on Philip's Blog
I really enjoyed your post and even though i didn't read it before the test, it would have probably helped me during the test. You pretty much said all the important aspects of the chapter but there was some key terms such as fertilization which you failed to mention. However everything else made crystal clear sense. In addition the diagram on Meiosis really made sense and helped me memorize and comprehend the steps. I had a better understand the differences between Meiosis and Mitosis. I also understand how meiosis can have anaphase 1 and anaphase 2, telophase 1 and 2 etc,even though i could used it for the test. I Also like how you put a great emphasis on Crossing Over, because it is a important part of meiosis. The videos that you posted, even though they were hard to find, i still enjoyed them because it told me a lot about meiosis and mitosis without me reading so much information. Chow, Chow, Chow, Chow!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
comment on philip's blog
Philip, everything you wrote seemed very helpful to me especially the little hints you would give about where on the test certain things would appear. It got me looking at almost everything the same way and if you posted somthing about fertilization and meiosis in plants and fungi and a comparison of mitosis and meiosis i think your blog would have been solid. But, the only regret i had after reading your blog was that i didn't read it sooner because i truly believe it would have helped me on the test. Hopefully your next blog would be just as good if not better.
comment on Philipos Blog

i would like to comment on Philip's blog about how cross over takes places. he was right about how it takes places, but could have gone more in depth about it.
Crossing over takes places in prophase 1 of meiosis 1. Chromosomal crossover is the process by which two homologous chromosomes exchange portions of DNA. Crossover usually occurs when portions of homologous chromosomes brake off and rejoin with other chromosomes. This is the exchange of genes, which is called genetic recombination.
Friday, December 14, 2007
I really enjoyed your lab and even though i didn't read it before the test, it would have probably helped me during the test. You pretty much said all the important aspects of the chapter but there was some key terms such as fertilization which you failed to mention. However everything else made crystal clear sense. The diagram was excellent because it explained everything that you said in writing but in a more visual way.
comment on Philipos Blog
I really enjoyed your lab and even though i didn't read it before the test, it would have probably helped me during the test. You pretty much said all the important aspects of the chapter but there was some key terms such as fertilization which you failed to mention. However everything else made crystal clear sense. In addition the diagram on Meiosis really made sense and helped me memorize and comprehend the steps. See YA
comment on CHAPTER 13
chapter 13
philip i liked the your post about meiosis and mitosis and the stages they go through. meiosis and mitsosis has much more then these process. you should've mentioned somethign about crossoverin detail for example it's a exchange of genetic material between homologues that occurs in prohase1 of meiosis 1. And also you should've talk msomethign about the three types of life cycle which are animal, fungi and plant. and their functions are: plant: alternation of generation, diploid stage is called sporophyte in which spores produce plant and haploid stage is gametophyte in which gametes produce plants divide mitotically. You should've mentioned some information about Asexual and sexual reproduction. I think that's about it philip
philip i liked the your post about meiosis and mitosis and the stages they go through. meiosis and mitsosis has much more then these process. you should've mentioned somethign about crossoverin detail for example it's a exchange of genetic material between homologues that occurs in prohase1 of meiosis 1. And also you should've talk msomethign about the three types of life cycle which are animal, fungi and plant. and their functions are: plant: alternation of generation, diploid stage is called sporophyte in which spores produce plant and haploid stage is gametophyte in which gametes produce plants divide mitotically. You should've mentioned some information about Asexual and sexual reproduction. I think that's about it philip
comment on Philips Blog
Philip, your information was very good and helpful, but I just wanted to add a little something. Meiosis occurs in organisms that reproduce sexually. Sexual reproduction is when two parents give rise to offsprings that have unique ccombination of genes inherited from the two parents. The role that meiosis takes in sexual reproduction is that it combines sets of genes from two different parents, forming genetically diverse offspring. This takes place in the sex cells.
Comment on Philips post
Philip, your post was very understandable and made clear sense. It would have been very helpful if you posted somthing talking about fertilization and meiosis in plants and fungi and a comparison of mitosis and meiosis for the test. Overall, yours did help with the multiple choice. Thank you
Dorathy
Dorathy
Thursday, December 13, 2007
comment on Roxxaine blog
i liked your blog because it was very interesting and the video you posted was very helpful to study the cycle.
Thursday, December 6, 2007
Part II Meiosis
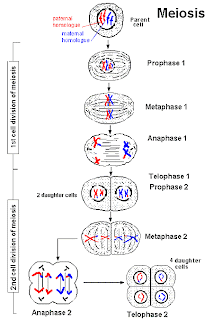
I am back again to now give everyone a quick summary on the second division of meiosis. This can also be called Gamete Formation. In prophase 2 the dna does not replicate, now entering metaphase 2, the chromosomes line up on the equator just like in the first divisional phase of meiosis. During Anaphase 2, the centromeres divide and each sister chromatid heads toward the opposite pole. Finally telophase 2 occurs and cell division is complete. Four haploid daughter cells now appear at the end of meiosis. Here is a picture that breaks down meiosis and that is the end of my post. Hopefully my post helped anyone in the class. New sherpa is Robert!
Part 1 of Meiosis
I am going to talk about some key parts of meiosis that everyone should know or hopefully will get a better understanding of after this discussion. Meiosis, a type of cell division, produces an egg and a sperm cell. Meiosis has two types of nuclear division. I will begin with interphase 1, though this starts before meiosis begins, the genetic material is duplicated/replicated. When the first division of meiosis begins, Prophase 1 will begin and this is where the chromatin condenses. Now, the most important part of Prophase 1 should start. The term is called CROSSING OVER. The meaning is as simple as the actual word. A exchange occurs between the two sister chromatids and the chromatids actually physically break off and then it is attached to a different homologous (same) chromosome. Everyone should know this term because most likely it will be on the test (probably short answer portion). Metaphase 1 now starts and this is when the homologous chromosomes line up in the equator (around the middle). Then the homologous pairs seperate but the sister chromatids stay together and this is called Anaphase 1. Last but not least, Telophase 1 begins and two daugther cells form. They have only one chromosome from the other homologous pair. I am not sure if this video will work on your computers but go ahead and try it but i would suggest watching it after i post part II of my discussion on meiosis. There are two websites, but i only will tell you one because the second one is right below it, hill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter12/animations.html. Paste this into google and there will be search results, click the one that says Biology 201(about the fourth or fifth result). Once the page loads, scroll down and you should see in bright red letters Too See an animation on meiosis go to: The third and fourth URL, are the two vids i wanted to show you. The third has audio and once you click it (pick the one that says, stages of meiosis) and the fourth does't have audio but both are great videos. Also be aware, if you are watching these videos in the school library that Ms. Johnson will probably activate VISION CONTROL , and when you try to explain that it is for school, it is already too late.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)